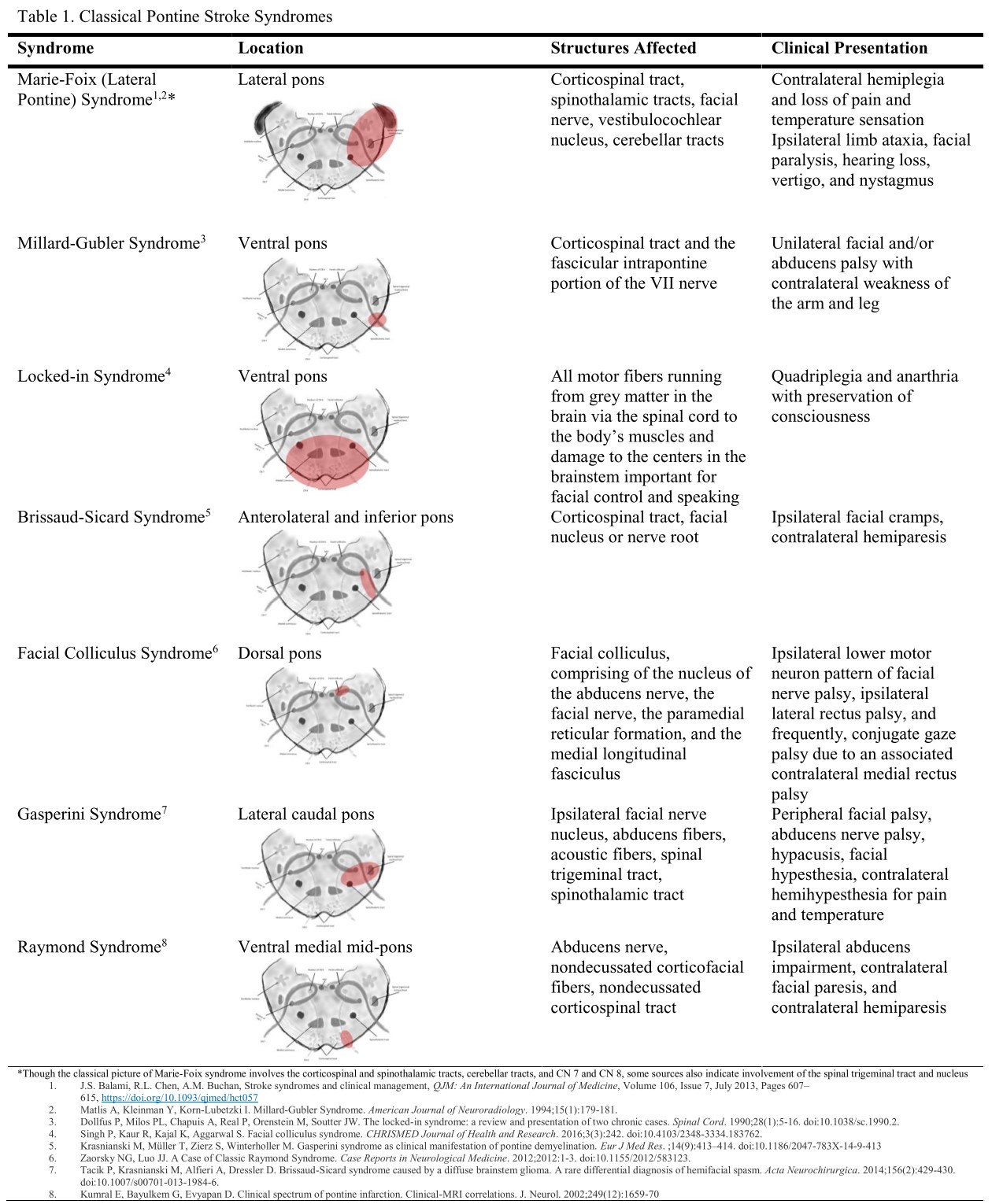
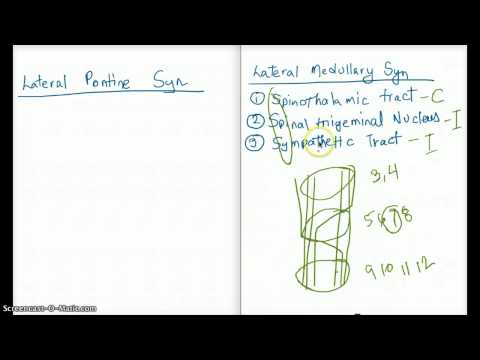
Lateral Pontine Syndrome Usmle
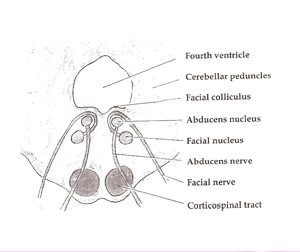
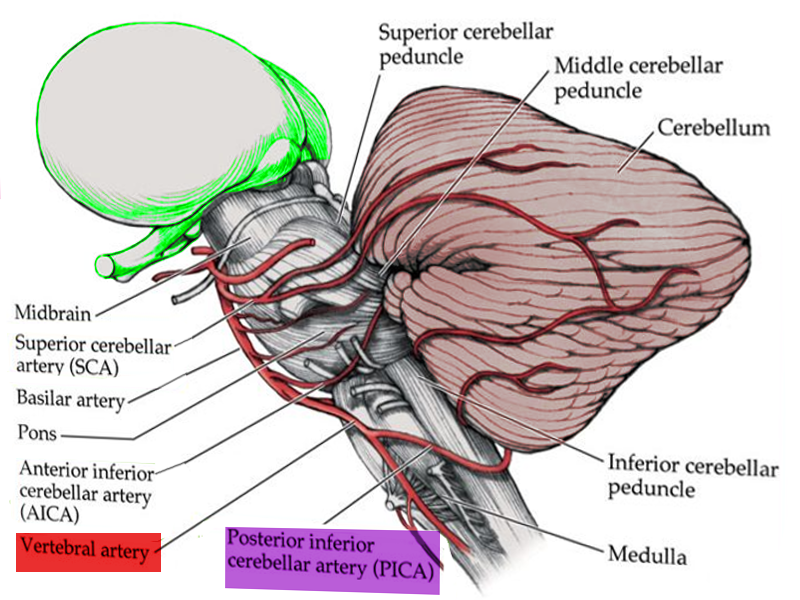
Lateral pontine syndrome usmle. PICA or the vertebral artery. These fibers however do not decussate so in a stroke of the lateral medulla the ipsilateral face is affected. Ipsilateral facial nerve paralysis facial nucleus and nerve fiber damage.
See lateral pontine syndrome below. Lenticulostriate arteries penetrating arteries. Occlusion is often caused by lipohyalinosis hyaline arteriosclerosis secondary to unmanaged hypertension.
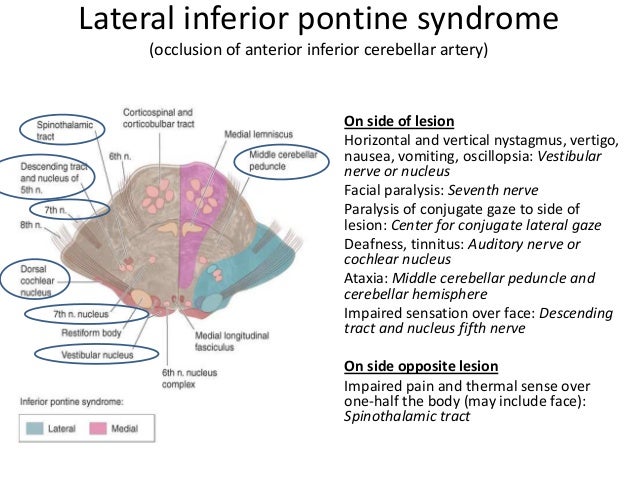
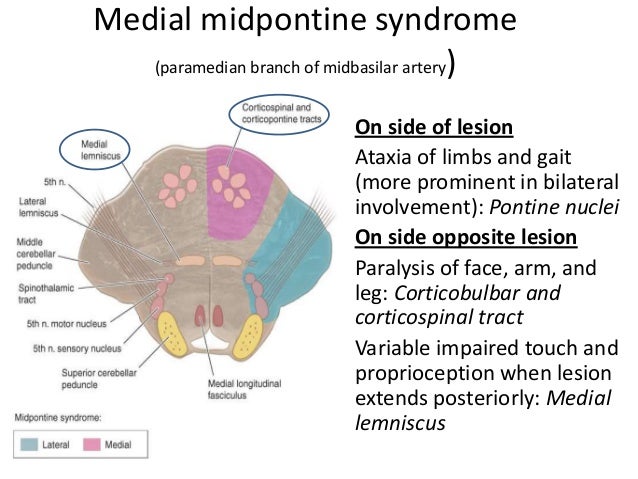
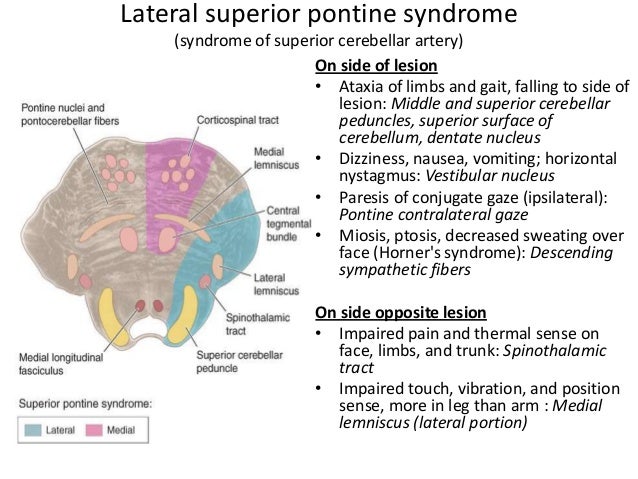
Occlusion of AICA can result in Lateral Pontine Syndrome or Marie-Foix syndrome. Management is supportive and may include swallowing and speech therapy as well as a feeding tube in some cases. These clinical manifestations except for the ipsilateral palatal and lingual disturbances were typical of the lateral inferior pontine syndrome caused by occlusion of anterior inferior cerebellar artery and the lesion was clearly demonstrated by horizontal and coronal MRI.
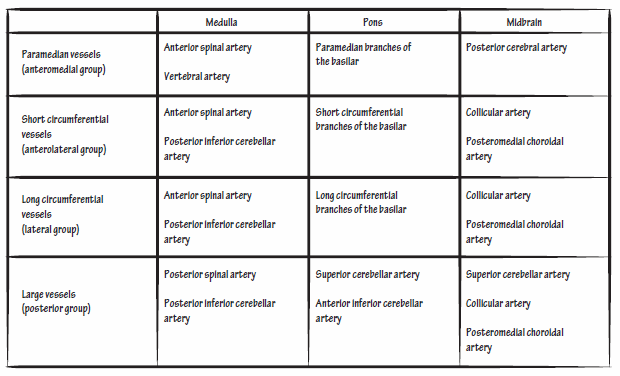
11 rows Circle of Willis. Lateral pons involving the. Anterior inferior cerebellar artery.
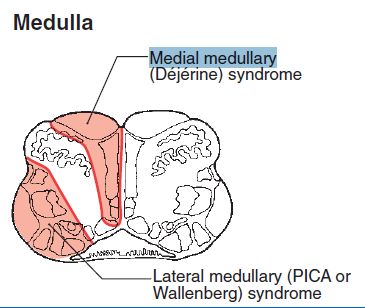
Visit the USMLE forum to talk about these and other USMLE test prep question banks. Lateral medullary syndrome Wallenberg syndrome. Free USMLE practice questions are provided by.
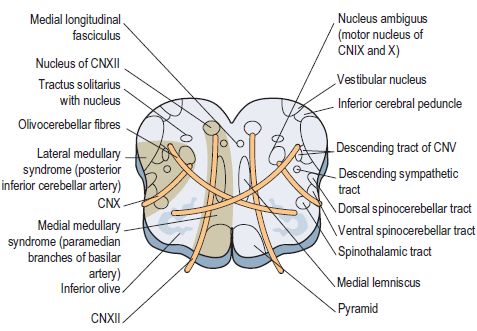
Biopsy demonstrates a nodular lymphoma with follicle formation. See lacunar syndromes below. Wallenberg syndrome lateral medullary syndromestroke refers to a cerebrovascular occlusion that occurs in either the vertebral artery or the posterior inferior cerebral artery PICA.
See below 9 Anterior inferior cerebellar artery. A patient presents with cervical lymphadenopathy.
Lenticulostriate arteries penetrating arteries.
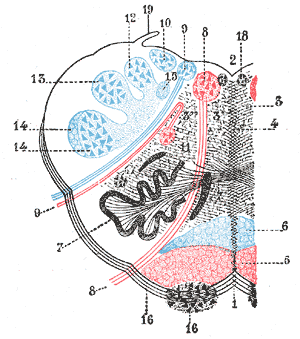
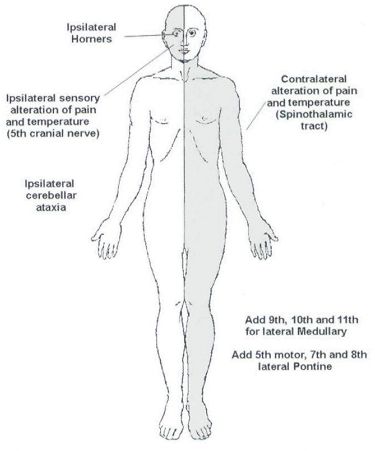
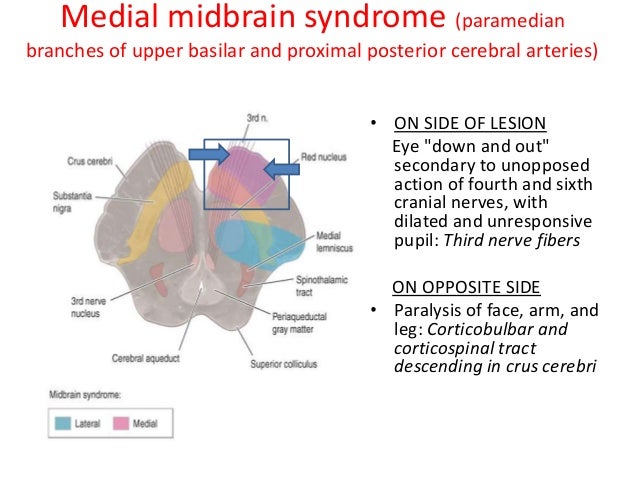
Ipsilateral loss of lacrimation and reduced salivation. It is estimated that there are around 600000 new cases of this syndrome in the United States alone. This condition is often caused by thrombosis or embolism however other causes such as syphilitic arteritis and vertebral artery dissection are also possible. One hallmark of brainstem strokes is the presence of long tract symptoms on one side and cranial nerve symptoms on the other side. 11 rows Circle of Willis. The pt is suffering from lateral medullary syndromewhich occurs due to lesion in PICA which arises from the vertebral artery What happens in PICA lesion. WHAT IS IT. Ipsilateral paralysis of the upper and lower face lower motor neuron lesion. These fibers however do not decussate so in a stroke of the lateral medulla the ipsilateral face is affected.
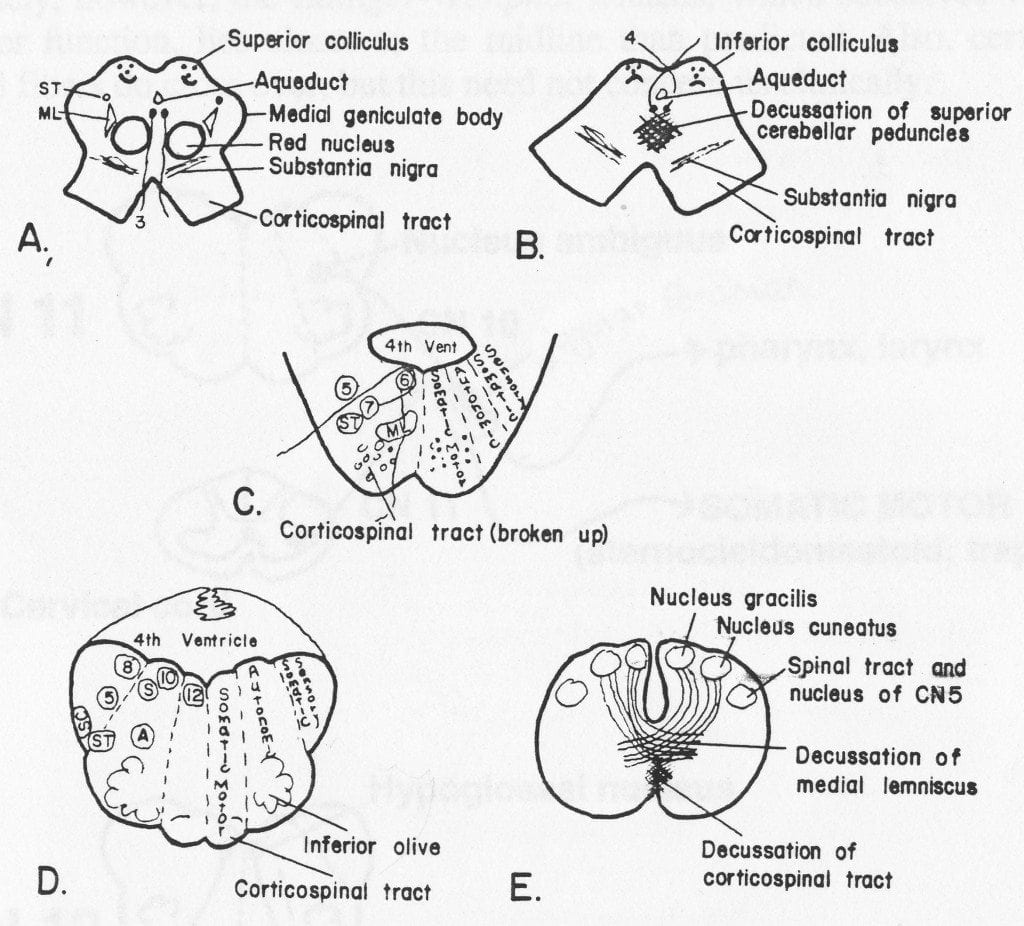
One hallmark of brainstem strokes is the presence of long tract symptoms on one side and cranial nerve symptoms on the other side. The red line indicates the level being described is the pons in this syndrome. WHAT IS IT. PICA or the vertebral artery. Facial paralysis salivation lacrimation and taste from the anterior tongue 23rd vertigo pain and temperature sensation of the. Lateral pons involving the. These clinical manifestations except for the ipsilateral palatal and lingual disturbances were typical of the lateral inferior pontine syndrome caused by occlusion of anterior inferior cerebellar artery and the lesion was clearly demonstrated by horizontal and coronal MRI.



























Post a Comment for "Lateral Pontine Syndrome Usmle"