What Is The Current Status Of Research On Marfan Syndrome
What is the current status of research on marfan syndrome. But in 2006 The Marfan Foundation formed a partnership with the National Heart Lung and Blood Institutes NHLBI Pediatric Heart Network to do something groundbreaking. Nutrition Weight and Quality of Life - Part 2 of 3. This Web page describes this and other areas of Marfan syndrome research.
The 8th symposium at the end of 2010 provides a useful summary of the current status of investigations reveals why life-expectancy has improved so markedly during the past 30 years and lays out a clear path for future endeavors not only in Marfan syndrome but in the expanding array of conditions related either through phenotype or pathogenesis. The diagnosis of Marfan syndrome continues to evolve. Recent research has revealed that these phenotypes are caused by mutations in fibrillin-1 the major structural component of elastic microfibrils and the continuing dysregulation of transforming.
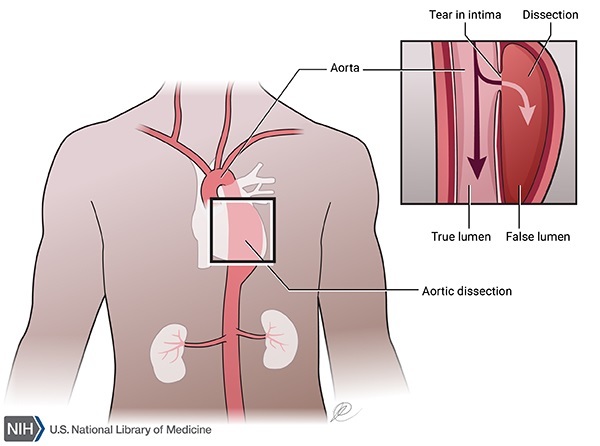
Research using the GenTAC registry found that women who have Marfan syndrome and who are pregnant or recently delivered are eight times more likely to have aortic dissection than women who have Marfan syndrome and are not pregnant or recently delivered. We recently shared Alix McLean Jennings story about how she worked with a nutritionist to bring her nine-year-old daughter Cassie who has Marfan syndrome up to a healthy weight. Recent research has revealed that these phenotypes are caused by mutations in fibrillin-1 the major structural component of elastic microfibrils and the continuing dysregulation of transforming growth factor beta TGFbeta signaling is principally considered to be contributing to the pathophysiological background of the disease.
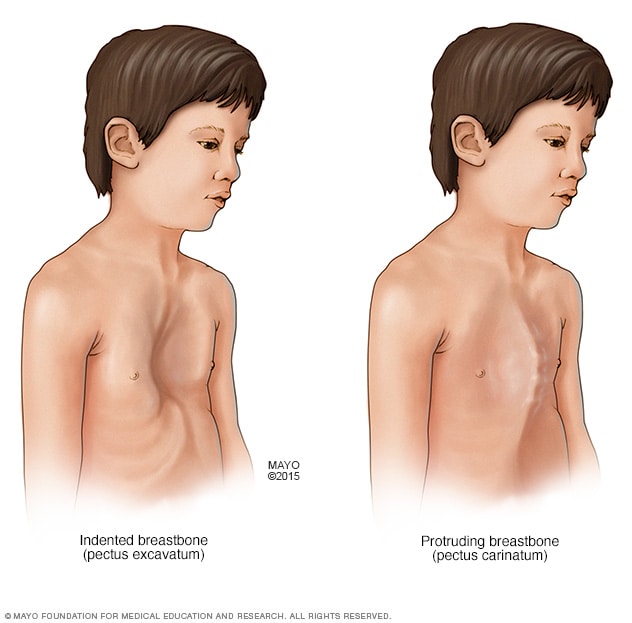
Often those affected by MFS are given heavy restrictions on exercise and physical activity because of heart bone and joint problems that commonly occur. Develop the largest-ever clinical trial for Marfan syndrome. A research article from the British Journal of Sports Medicine examined the proper exercise precautions for people with Marfan Syndrome MFS.
As this eMedTV article explains a current area of Marfan syndrome research focuses on finding ways to treat the complications that arise in people with the disorder. This research study found that those with MFS should be allowed and encouraged to engage in normal. The bottom line is that Marfan syndrome is a dominant genetic trait and that everyone can inherit it under certain circumstances Birth Defects.
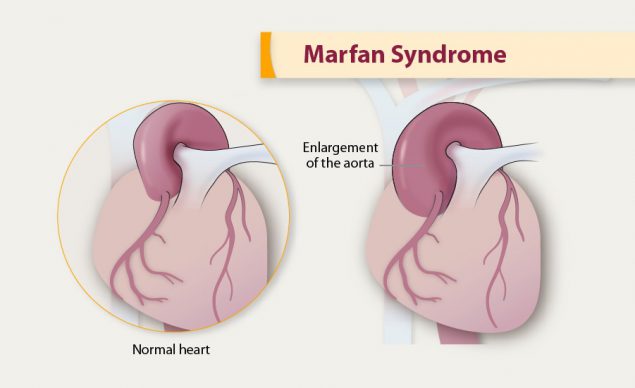
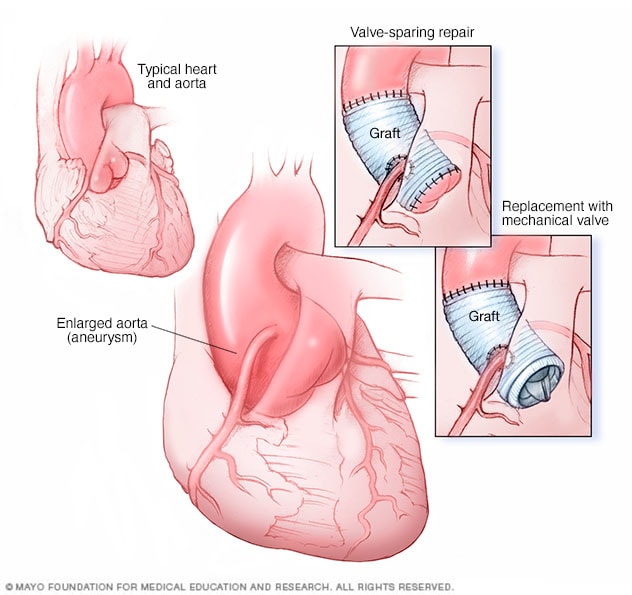
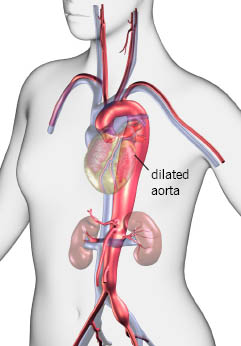
An investigational treatment for Marfan syndrome is as effective as the standard therapy at slowing enlargement of the aorta the large artery of the heart that delivers blood to the body new research shows. The findings indicate a second treatment option for Marfan patients who are at high risk of sudden death from tears in the aorta. Existing criteria 89 are in the process of being revised based on a workshop held in Brussels Belgium in early 2007.
Today in The Marfan Blog we share the first part of Alixs Q A with her nutritionist Hien. The major component of structures in our tissues called microfibrils.
The 8th symposium at the end of 2010 provides a useful summary of the current status of investigations reveals why life-expectancy has improved so markedly during the past 30 years and lays out a clear path for future endeavors not only in Marfan syndrome but in the expanding array of conditions related either through phenotype or pathogenesis.
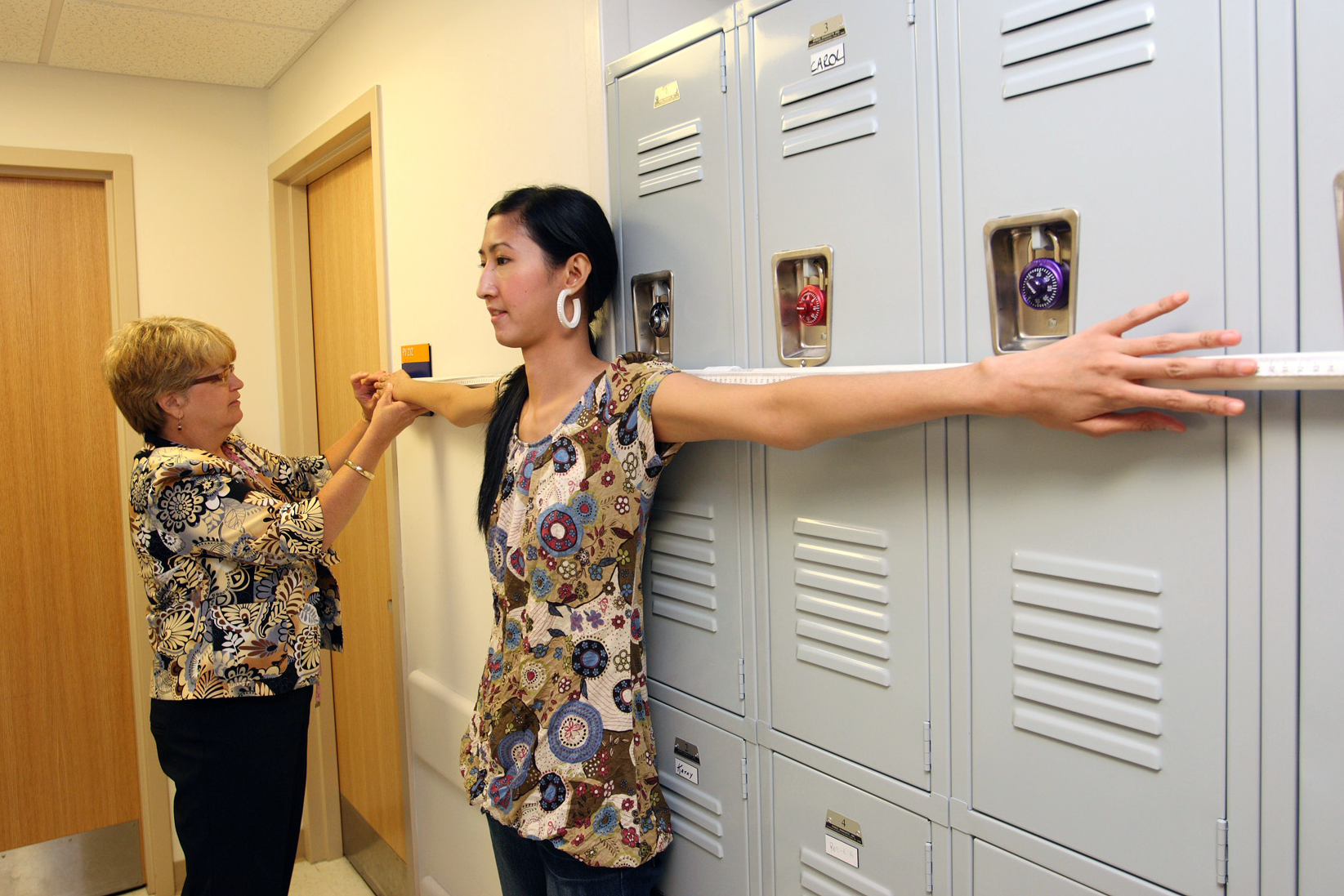
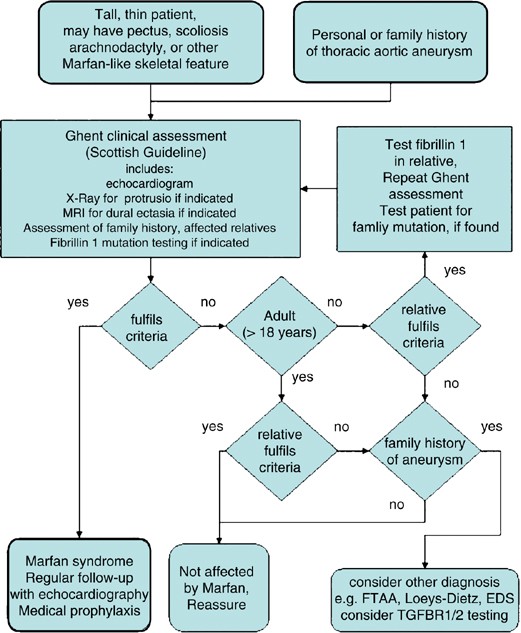
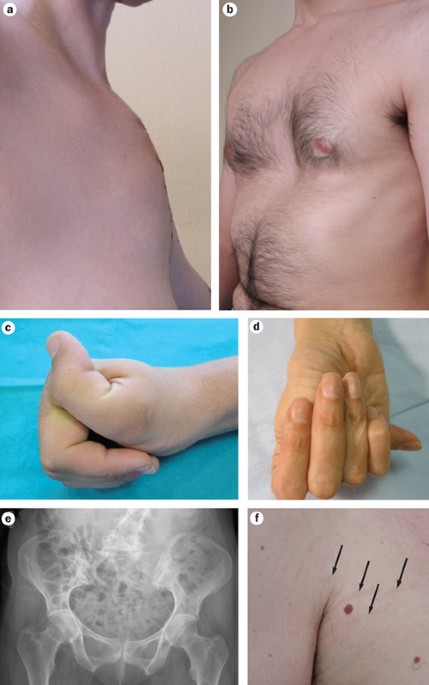
This Web page describes this and other areas of Marfan syndrome research. Existing criteria 89 are in the process of being revised based on a workshop held in Brussels Belgium in early 2007. Marfan syndrome is an autosomal dominant disorder characterized by tall stature long arms and legs ectopia lentis and aortic aneurysms and dissections. Both clinical and molecular genetic criteria have a role in assigning the label of Marfan syndrome with confidence. The bottom line is that Marfan syndrome is a dominant genetic trait and that everyone can inherit it under certain circumstances Birth Defects. By Julia Evangelou Strait November 18 2014. The findings indicate a second treatment option for Marfan patients who are at high risk of sudden death from tears in the aorta. Marfan syndrome is a highly variable disease cause by mutations that affect the protein fibrillin-1. Finally being the fourth reason current research is still underway despite the fact that there is no cure yet.
By Julia Evangelou Strait November 18 2014. Recent research has revealed that these phenotypes are caused by mutations in fibrillin-1 the major structural component of elastic microfibrils and the continuing dysregulation of transforming growth factor beta TGFbeta signaling is principally considered to be contributing to the pathophysiological background of the disease. The findings indicate a second treatment option for Marfan patients who are at high risk of sudden death from tears in the aorta. This Web page describes this and other areas of Marfan syndrome research. Research using the GenTAC registry found that women who have Marfan syndrome and who are pregnant or recently delivered are eight times more likely to have aortic dissection than women who have Marfan syndrome and are not pregnant or recently delivered. We always work tirelessly to advance research that saves lives and dramatically enhances the quality of life for people living with Marfan syndrome and related conditions. An investigational treatment for Marfan syndrome is as effective as the standard therapy at slowing enlargement of the aorta the large artery of the heart that delivers blood to the body new research shows.
























:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-6396127831-ac72ad703f264194ac1b7c5e4ce5aa3b.jpg)









Post a Comment for "What Is The Current Status Of Research On Marfan Syndrome"